5 things to avoid to manage geographic atrophy
When dry age-related macular degeneration progresses to an advanced stage, it is known as geographic atrophy (GA). It is called “geographic” because the regions of atrophy look similar to a map when a doctor examines the retina. GA reduces a person’s ability to read, drive, and recognize faces by affecting their central vision. While GA cannot be cured entirely, here are a few things to avoid to slow down its progression:
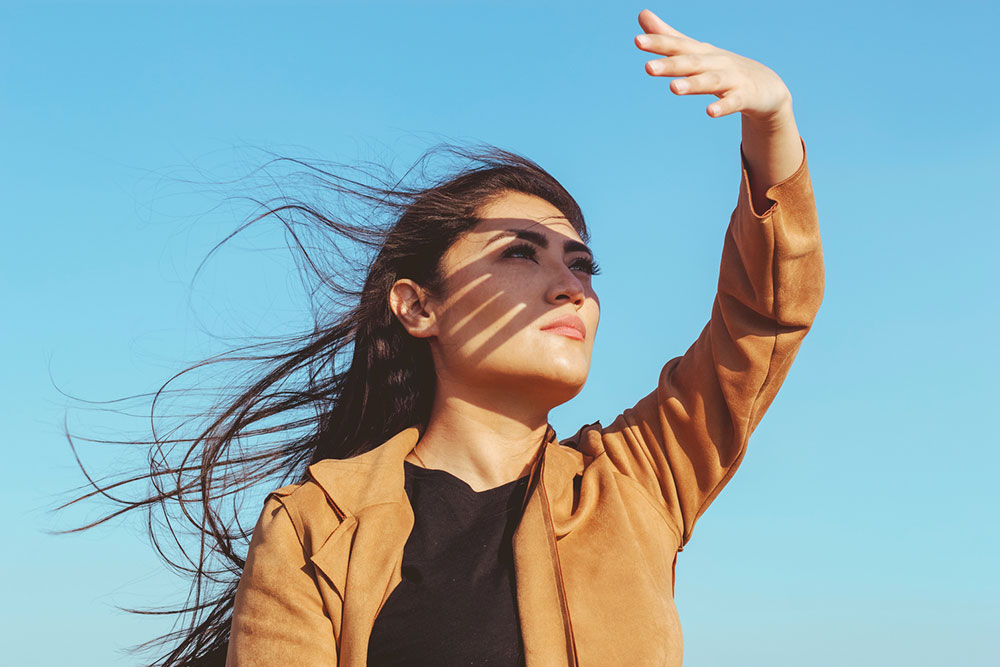
Exposure to sun
The sun’s ultraviolet light can have harmful effects on the eyes. This will cause GA to progress quickly. So, one should avoid stepping out in the sun as much as possible. If going out is unavoidable, it is best to wear sun protection. These include sunglasses that have UV protection and a wide-brimmed hat.
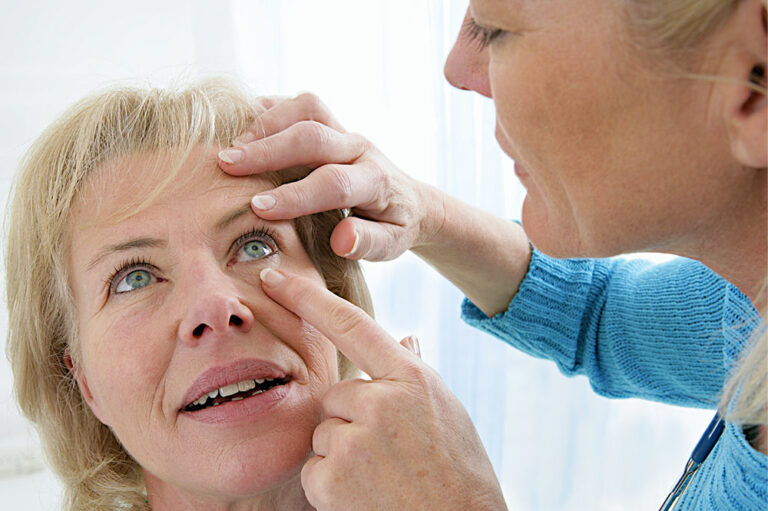
Irregular eye check-ups
With GA, it is important to monitor the progression of the disorder. This can help in taking measures that can help in effectively managing the condition. However, this is only possible when one schedules and attains regular eye check-ups. Therefore, missing out on eye appointments is one of the major things to avoid if one wants to take better care of their eyes with GA.
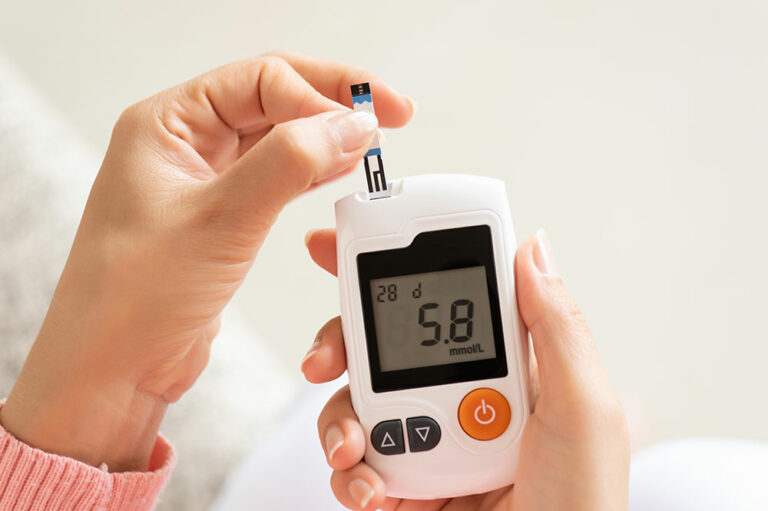
High blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Hypertension or high blood pressure can cause faster degeneration of the retina. Furthermore, high cholesterol levels can cause dysfunction of the retina by damaging the blood vessels. Therefore, it is crucial to regularly monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels to manage GA effectively.
Sedentary lifestyle
Maintaining an exercise routine can have a positive impact on protecting overall eye health. It can also aid in slowing the progress of GA. It is important to engage in moderate exercises for at least five days a week. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle without physical activity can raise cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure levels, making it harder to manage GA.
Fast foods
Fast foods such as fried chicken, French fries, and pizza are often loaded with high amounts of carbohydrates and sugar but are low in fiber. Additionally, such foods are high in saturated fats and sodium and are highly processed, which can lead to blood lipid imbalances, high blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. All of these factors can make it difficult to properly manage the symptoms of GA.