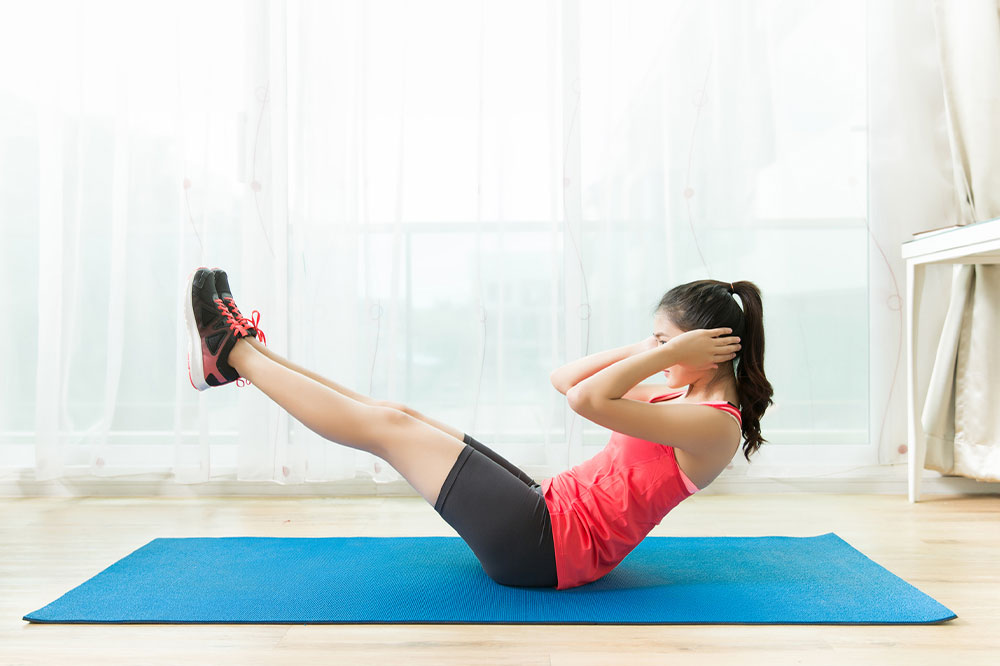
Exercise – An effective solution in cancer management
In the past, doctors typically advised cancer patients to rest and avoid physical activity. However, early exercise cancer research (or research oncology) in the 1990s and 2000s contradicted this advice. This field has grown exponentially over the past decade, with over 1000 randomized controlled trials. Evidence now overwhelmingly suggests that those living with cancer can greatly benefit from being physically active. Therefore, exercise can now be precisely prescribed to address several cancer-related conditions.
How does exercise help mitigate cancer-related outcomes?
Studies in exercise oncology can be traced back to the 1980s when research by a leading state university found that breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy who exercised daily experienced less fatigue, nausea, and disability from the treatments. This kickstarted research in the field to find out the relationship between exercise and cancer.
In 2019, a panel of experts found that doing half an hour of aerobic exercise three times a week during and after cancer treatment can ease fatigue, anxiety, and depression and improve quality of life and physical functioning. The panel also concluded that there was no increased risk of lymphedema from resistance exercise twice a week.
However, researchers do currently lack evidence as to whether exercise can help improve other health outcomes such as peripheral neuropathy, cardiotoxicity, cognitive functioning, pain, or chemotherapy completion rate.
How can exercise be used as a preventive tool against cancer?
Studies strongly suggest that exercise can help reduce the risk of seven types of cancer: bladder, breast, colon, endometrial, esophageal, kidney, and stomach. It has also been linked to the prevention of lung, blood, head, neck, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancers. Exercise has also reduced the risk of fatalities in people diagnosed with breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers in the range of 40% to 50%.
Experts believe that this is because exercise helps reduce levels of inflammation and insulin, which have been directly linked to some cancers. It also induces angiogenesis, or the creation of new blood vessels, which could mean that more blood-driven anti-cancer treatment can be delivered to malignant tumors.
Why does exercise help?
Exercise alone cannot cure cancer, but it can be helpful in the process. While cancer weakens the immune system, every single round of exercise works wonders to bolster it. Research has found that pedaling full-speed on a stationary bike for 10 minutes can boost tumor fighters called natural killer cells by 10 times in the body, while also having a positive impact on protective T and B cells in the blood.
By using exercise to help cancer patients build up bigger armies of defender cells, it may be possible to make powerful immunotherapy treatments work better. Along with cutting calories, exercise can also help reduce body fat, which is a common concern for many breast cancer patients, and linked to reduced self-esteem and poor quality of life. Working with nutritionists, behavioral psychologists, fitness experts, and exercise oncologists, together with specialists, can help pave the way for cancer remission.